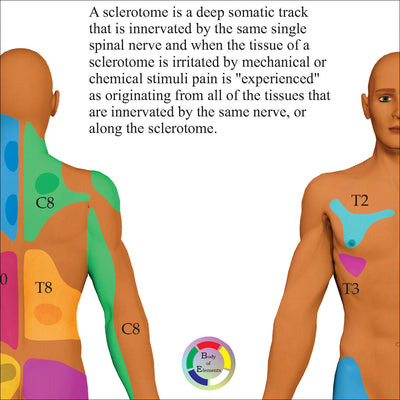
What is the significance of sclerotome pain referral patterns?
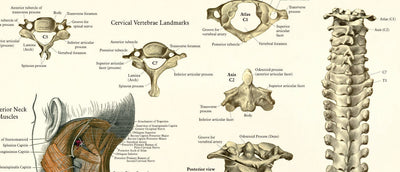
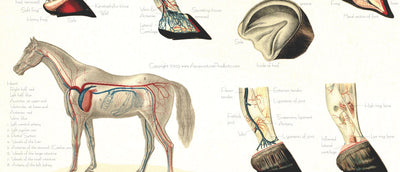
Sclerotome pain referral patterns are important in both clinical diagnosis and manual therapies because they help identify deep, diffuse pain that originates from bone or periosteal (connective tissue) structures innervated by a single spinal nerve root. Unlike dermatomes (skin) and myotomes (muscle), sclerotomes relate to deep tissues like ligaments, fascia, periosteum, and joint capsules.
1. Diagnostic Tool for Nerve Root Involvement
Pain that follows a sclerotomal pattern may indicate irritation or compression of a specific spinal nerve root, often due to: Disc herniation,
Foraminal stenosis, Degenerative joint disease or Tumors or infections affecting the spine
2. Helps Differentiate Types of Pain
Sclerotomal pain is typically: Deep, dull, and poorly localized. Often described as “achy” or “boring”
In contrast: Dermatomal pain is sharp, burning, and well-defined. Myotomal pain is crampy and associated with movement or fatigue
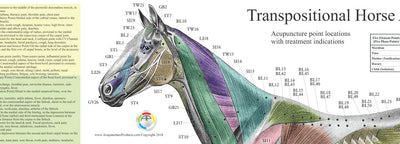
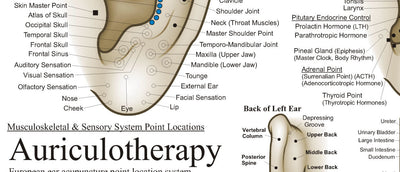
3. Guides Manual Therapy and Acupuncture
Understanding sclerotomal patterns helps target: Referred pain from joints (e.g., facet joints, SI joint). Pain syndromes like whiplash or chronic low back pain. Acupuncture points that treat deep connective tissue pain
4. Important in Referred Pain Mapping
Sclerotomal maps assist clinicians in tracing the origin of pain that doesn’t follow a typical dermatome or myotome, such as: Pain around the shoulder blade from lower cervical irritation or Deep pelvic pain from sacral sclerotome involvement.
Key Clinical Takeaway
If a patient reports deep, vague, hard-to-localize pain, particularly around a joint or bony prominence, and imaging is inconclusive, consider sclerotomal referral in your differential diagnosis. It can point toward spinal nerve root involvement, even in the absence of neurological deficits.